

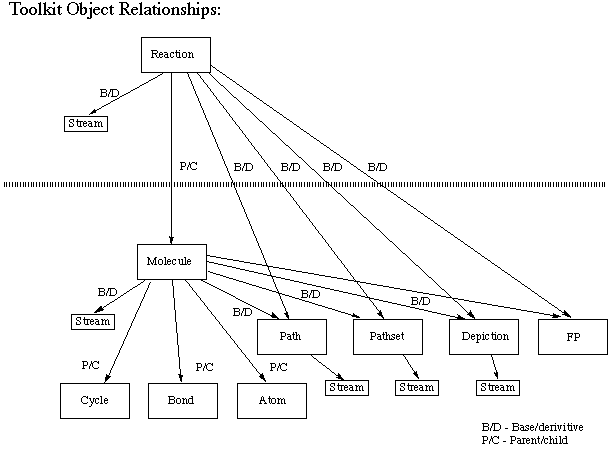
Children of a parent are normally accessed with dt_stream().
The parent of a child is accessed with dt_parent().
Modification of the base object causes any derivatives to be deallocated.
One can't get access to all of the derivatives of a given base object
(eg. all depictions of a molecule).
The base of any given derivative object is accessed with
dt_base().
A parent/child example (molecule/atoms):
void do_stuff(dt_Handle ob)
{
dt_Handle atoms, atom, myparent;
atoms = dt_stream(ob, TYP_ATOM);
while (NULL_OB != (atom = dt_next(atoms)
{
/*** perform operations on each atom ***/
...
myparent = dt_parent(atom);
}
dt_dealloc(atoms);
return;
}
A base/derivative example (molecule/depiction):
void do_other_stuff(dt_Handle ob)
{
dt_Handle depiction, mybase;
depiction = dt_alloc_depiction(ob);
...
dt_calcxy(depiction);
dt_depict(depiction);
...
mybase = dt_base(depiction);
return;
}